People often say that a Foundation is the civil law alternative to a Trust; but what does this mean? What does a Foundation offer your clients that a Trust cannot? Furthermore, when does it make sense to use a Foundation? Add on top of that the fact that you can validly use both entities in tandem, the clear contrast we were hoping for begins to look grey – but hopefully this article can provide some clarity.
This is the third article in a three-part series we have produced on Foundations. If you would like to reacquaint yourself with the basics of Isle of Man Foundations or the technicalities of setting up and administering one, please refer back to the previous articles in this series:
- Isle of Man Foundations for Offshore Planning – An Introduction (Article 1 of 3)
- Establishing and Administering an Isle of Man Foundation (2 of 3)
In this article we will be examining some of the most common uses of Isle of Man Foundations (IOM Foundations), which includes:
- Using an Isle of Man Foundation for Succession Planning
- Using an Isle of Man Foundation for Asset Protection
- Using an Isle of Man Foundation as Trustee
- Using an Isle of Man for Charitable Objects
- Dixcart Supporting the Establishment and Administration of Foundations
Using an Isle of Man Foundation for Succession Planning
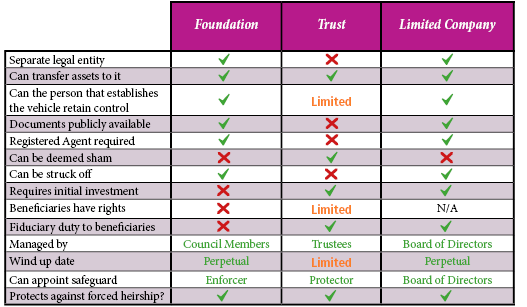
Unlike a Trust, an IOM Foundation is an incorporated vehicle, having separate legal personality; similar to a Private Limited Company, but without shareholders. As such, the IOM Foundation has the capacity to enter into contract, own property and take legal action in its own right.
As an Isle of Man corporate vehicle the IOM Foundation is a ‘Corporate Taxpayer’ under s120(ba) of the Income Tax Act 1970, and benefits from the local tax regime, boasting headline rates such as:
Because an IOM Foundation is not answerable to shareholders and is perpetual in term, it is free to pursue its Founder’s intended Objects for as long as stipulated in the Foundation Rules. For these reasons, the IOM Foundation can be a great choice for those seeking to ensure the continuation of their life’s work, whether a successful business or charitable pursuits.
The IOM Foundation can be established for the purpose of purchasing and owning the shares of a company, either retaining profits for future growth or making distributions to classes of beneficiary, in line with the IOM Foundation’s Instrument and Rules.
Furthermore, once the IOM Foundation has been registered, unlike a Trust, it will receive a certificate of incorporation, which can be useful for evidencing existence when dealing with institutional lenders and third parties, for example. To this end, an IOM Foundation could be used as a Special Purpose Vehicle, with one of its Objects being to secure capital for the business via loans that will not appear on the company’s balance sheet.
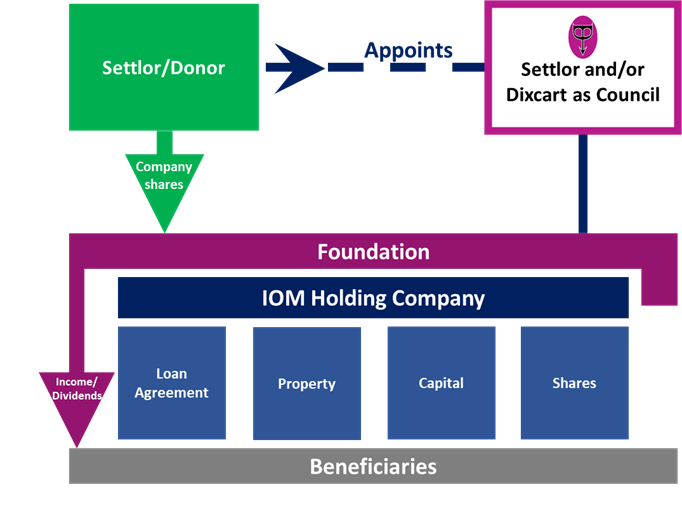
IOM Foundations can deliver a level of assurance and control that make them an ideal vehicle for succession planning.
Using an Isle of Man Foundation for Asset Protection
One of the most common uses of the IOM Foundation is asset protection, particularly with regards to Estate Planning. The Founder can dedicate assets (usually capital) into the corporate vehicle. Following this, the Foundation Council will manage and distribute the funds in line with the Foundation Rules and Instrument, as prescribed by the Founder.
Non-charitable IOM Foundations require an Enforcer to be appointed, who ensures the Council carries out its functions in compliance with the constitutional documents. Whilst the Founder can be appointed as Enforcer, it is recommended that they are not; very often it will be a trusted adviser who might act as Enforcer. However, the Founder can be, and often is, appointed as a Council Member; allowing them to retain some control to ensure that their goals come to fruition, potentially without jeopardising their tax position.
Not only does the IOM Foundation provide a clear and enforceable roadmap for the Council Members to follow, due to its legal personality it might also be used to mitigate tax liabilities, particularly inheritance and wealth taxes. The IOM Foundation will be domiciled in the Isle of Man, therefore being subject to the Manx tax regime i.e. 0% IHT, for example.
The IOM Foundation is also appropriate for the mitigation of Forced Heirship laws. As the structure is resident in the jurisdiction of registration, therefore the laws of the Isle of Man are applicable. Any challenge to the IOM Foundation will be heard in an Isle of Man Court and, for example, laws seeking to challenge the validity of the IOM Foundation can be set aside, in conformity with the Foundations Act 2011.
IOM Foundations are not currently a matter of public record, meaning the identities of the Founder, and any Donors or Beneficiaries are a private matter.
Depending on the IOM Foundation’s constitution, the Foundation’s Rules which will deal with the appointment or removal of any parties, such as Enforcer, Beneficiaries etc., can be altered at any time. This flexibility allows for any change in wishes or circumstance.
The IOM Foundation can also be used to ringfence assets and wealth exposed to both creditors or spouses etc. making it a great all-round tool for asset protection.
Using an Isle of Man Foundation as Trustee
Both Foundations and Trusts provide mechanisms for the transfer of beneficial ownership, from donor to beneficiary – this may make it seem like it’s always an either-or scenario, but it isn’t. In some circumstances the two vehicles can complement one another to further meet the client’s objectives.
The IOM Foundation can be appointed as Trustee, providing a function similar to a Private Trust Company. This provides some or all of the benefits of appointing a Professional Trustee, depending on the choice of Council Members. Such benefits can include:
- Continuity
- Neutrality
- Technical Knowledge
- Mitigating Risk
In addition, the Settlor can also be appointed as Council Member to retain some oversight, ensuring the purpose of the Trust is realised. This may provide the Settlor with some degree of comfort following the transfer of his assets to a new fiduciary service provider.
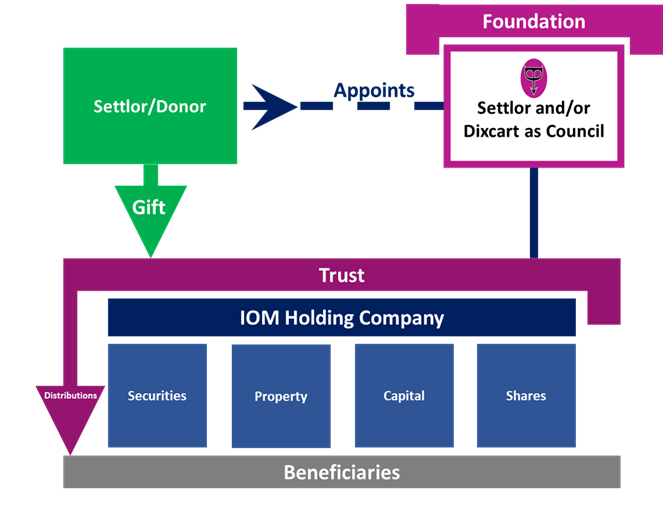
As you can see, using the two entities in tandem can help deliver added flexibility with regards to activity and increased oversight concerning the purpose in mind.
Using an Isle of Man Foundation for Charitable Objects
The IOM Foundation is also commonly used as a philanthropic vehicle. The IOM Foundation can be either dedicated to charitable or a mixture of charitable and non-charitable Objects. If established for purely philanthropic pursuits, the IOM Foundation’s Objects cannot be altered to include non-charitable activities in the future.
The IOM Foundation may be of particular relevance to clients seeking to engage in philanthropic activities in jurisdictions that do not recognise trusts.
There are broadly two categories of charitable IOM Foundation, each with its own purpose:
- A non-operating charitable IOM Foundation is established to make grants to other not-for-profit or charitable organisations. In practice this may be the donation of income from its underlying assets or further donations from the Founder/Donors, or blend. Classes of Beneficiaries can be limited to a single organisation or cause as desirable.
- An operating charitable IOM Foundation seeks to engage in charitable activities directly, taking responsibility for fulfilling its charitable Objects. Examples of such operating charitable IOM Foundations include; museums, educational institutions, and community initiatives.
The IOM Foundation can be used flexibly for the benefit of whatever cause or organisation is close to the Founder’s heart.
Dixcart Supporting the Establishment and Administration of Foundations
At Dixcart, we offer a full suite of offshore services to advisers, and their clients, when considering the establishment of an IOM Foundation. Our in-house experts are professionally qualified, with a wealth of experience; this means we are well placed to support and take responsibility for different roles, including acting as Council Member, as well as providing specialist advice when required.
From pre-application planning and advice, to the day-to-day administration of the Foundation, we can support your goals at every stage.
Get in touch
If you require further information regarding Isle of Man Foundations, their establishment or management, please feel free to get in touch with Paul Harvey at Dixcart: advice.iom@dixcart.com.
Dixcart Management (IOM) Limited is licensed by the Isle of Man Financial Services Authority.